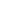
An oil-immersed type transformer is a common piece of electrical equipment used to convert electrical energy from one voltage level to another. The oil-type transformer working principle is based on the principles of electromagnetic induction and energy transfer.
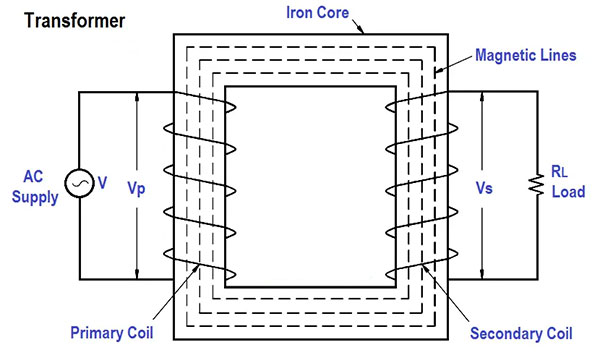
Oil-immersed transformers are mainly composed of two coils, one is the main coil (also known as the high-voltage coil), and the other is the secondary coil (also known as the low-voltage coil). The two coils are connected to each other through the iron core.

When high-voltage current passes through the main coil, the generated magnetic field is conducted to the secondary coil through the iron core. The conduction of this magnetic field causes the voltage in the secondary coil to change, converting electrical energy from high voltage to low voltage.