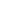
A transformer is an integral key device in a power system, used to transfer electrical energy from one voltage level to another. In the design of transformers, there are two common types: dry-type transformers and oil-immersed transformers.
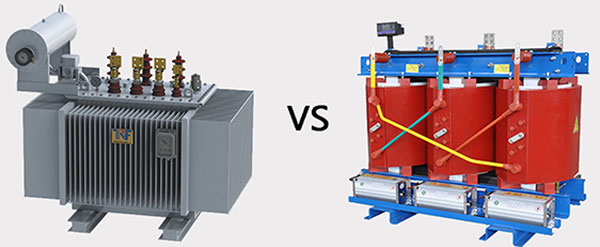
First of all, a dry-type transformer is a transformer that does not contain oil. It uses dry insulation to insulate and protect the coils. This type of transformer is commonly used in indoor applications such as commercial buildings, hospitals, and schools. A significant advantage of dry-type transformers is the lack of maintenance and the hassle of handling oil. Plus, they don’t produce harmful gases or liquids, making them more environmentally friendly. However, dry-type transformers are generally larger, heavier, and more expensive than oil-filled transformers.
In contrast, oil-filled transformers use insulating oil to cool and insulate the coils. This type of transformer is often used outdoors or in large power systems. The main advantages of oil-immersed transformers are their efficient cooling capabilities and smaller size. Due to the better cooling effect of the oil, oil-immersed transformers can withstand higher loads and short-term overloads. In addition, oil can also provide better insulation properties, making transformers more reliable in harsh environments. However, oil-immersed transformers require regular maintenance and monitoring of oil quality to ensure their proper operation.

To sum up, there are differences between dry-type transformers and oil-immersed transformers in terms of design, application, and maintenance. Which type of transformer to choose depends on specific application needs and budget constraints. Whether it is a dry-type transformer or an oil-immersed transformer, they all play an important role in the power system to ensure the effective transmission and distribution of electric energy.