As a stable source of electricity, diesel generators are widely used in many occasions. However, under different load conditions, the diesel generators frequency adjustment may fluctuate, which will affect the stability of electricity and thus the normal operation of equipment. It is crucial to understand the diesel generators frequency regulation method, especially in situations with high-precision electricity demand. This article will introduce the regulation principle of diesel generator frequency, common methods and precautions during the regulation process.
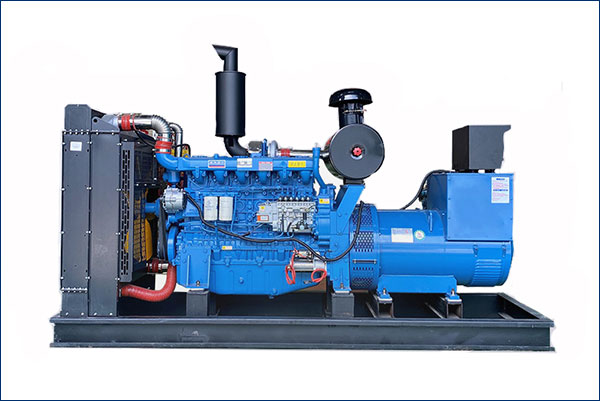
1. Basic principles of diesel generator frequency
The diesel generator frequency is directly related to its speed, and the frequency (Hz) is determined by the engine speed and number of poles. Usually, the rated frequency of a diesel generator is 50Hz or 60Hz, depending on the regional power grid standard. In order to maintain frequency stability, the diesel generator must maintain a constant speed. However, changes in external loads often cause speed fluctuations, so frequency regulation is required.
2. The importance of frequency regulation
Frequency stability is essential for the smooth operation of the power system. If the frequency is too high or too low, it will not only affect the normal operation of the connected equipment, but may also cause power waste or equipment failure. Therefore, frequency regulation is a key link in the diesel generator system, especially in places such as industry, medical care, and data centers that require high-precision electricity.
3. Common frequency regulation methods
There are many ways to regulate the frequency of diesel generators. The following are several main regulation methods:
Electronic speed governor regulation
The electronic speed governor controls the engine speed by adjusting the fuel injection amount to stabilize the frequency. This method responds quickly and is suitable for occasions with large load fluctuations.
Mechanical speed governor regulation
The mechanical speed governor adjusts the fuel supply through the principle of centrifugal force to keep the speed constant. Although the mechanical speed governor responds relatively slowly, it has a simple structure and low cost, and is suitable for applications where the load changes little.
Load distribution and parallel operation
When multiple diesel generators are operated in parallel, the frequency can be adjusted by load distribution control. The control system adjusts the output power of each generator according to the real-time load to keep the frequency stable.
4. Steps for diesel generator frequency regulation
In actual applications, diesel generator frequency regulation generally includes the following steps:
Preliminary inspection: Make sure that the diesel generator has sufficient fuel supply and all electrical connections are normal.
Set target frequency: Set the target frequency of the diesel generator according to the equipment requirements (usually 50Hz or 60Hz).
Adjust the speed governor: When the load changes, the speed is kept constant by adjusting the speed governor.
Monitor frequency fluctuations: Monitor frequency fluctuations in real time during operation to ensure that the fluctuation range is within the acceptable error range.
Frequency fine-tuning: When the accuracy requirement is high, fine-tune the frequency to ensure frequency stability.
5. Precautions in frequency regulation
When performing frequency regulation, the following points should be noted:
Avoid frequent adjustments: Frequent adjustments will cause unstable engine load, which will affect the life of the diesel generator.
Load matching: When adjusting the frequency, sudden load changes should be avoided, otherwise the frequency may fluctuate greatly.
Regular maintenance: The governor and fuel system need to be regularly inspected and maintained to ensure the stability of their regulation function.
6. Future technical trends in frequency regulation
With the development of intelligent technology, more and more diesel generators are beginning to apply intelligent control systems to achieve more accurate frequency regulation. For example, modern diesel generators are equipped with automatic frequency regulation systems, which can automatically adjust the frequency according to load changes. In addition, some new diesel generators also use remote monitoring technology, which allows operators to monitor and adjust the frequency in real time, further improving the convenience and accuracy of frequency regulation.
Conclusion
Diesel generator frequency regulation is a key link in ensuring the stability of the power system. Through the correct adjustment method and modern control technology, diesel generators can maintain stable frequency under various load conditions and provide reliable power supply for equipment. Choosing the right frequency adjustment method will help improve the efficiency and life of diesel generators.