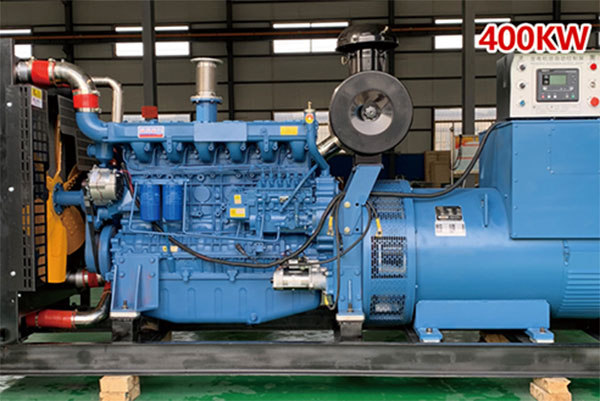
Diesel generators are a crucial power source for various industries, providing reliable electricity in both primary and backup applications. Understanding the starting process of a diesel generator can help users maintain their equipment more effectively and ensure smooth operation during critical times. This blog will break down the starting sequence, highlight essential components, and provide tips for efficient and trouble-free operation.
The Basics of Diesel Generator Starting
Before diving into the technical process, it’s important to understand the core principle of how a diesel generator operates. Unlike gasoline engines, diesel engines rely on compression ignition. This means the air inside the engine cylinder is compressed to extremely high levels, raising its temperature. When fuel is injected into this heated air, it ignites and powers the engine.
To initiate this process, the generator goes through a series of precise steps, involving mechanical, electrical, and electronic systems working in unison.
Step 1: Pre-Start Checks
Before starting a diesel generator, certain preparatory steps are essential. These include:
- Fuel Level Inspection: Ensuring there is sufficient diesel fuel in the tank is critical. Low fuel levels can result in air entering the fuel system, causing potential startup issues.
- Oil and Coolant Levels: Both oil and coolant are vital for the generator’s operation. They prevent overheating and reduce friction between moving parts.
- Battery Charge: The starting system relies on a charged battery. If the battery voltage is low, the generator may fail to start.
Regularly conducting these checks reduces the risk of unexpected malfunctions and extends the lifespan of your generator.
Step 2: Activation of the Starter Motor
Once the pre-start checks are complete, the starting sequence begins. Most diesel generators use an electric starter motor to crank the engine. This motor draws power from the battery and turns the engine’s flywheel, which initiates the compression process.
- Glow Plugs or Heaters: In colder climates, glow plugs or intake heaters may activate during this stage. These components warm the air in the cylinder, making it easier for the engine to start.
- Control Panel Signals: Modern generators often have control panels that display status messages or alarms. Before proceeding, operators should ensure no warnings are active.
Transitioning from this stage to the next requires careful monitoring to avoid unnecessary strain on the system.
Step 3: Fuel Injection and Ignition
The heart of the starting process lies in fuel injection. During cranking, the fuel injectors spray diesel into the heated, compressed air within the cylinder. This action triggers combustion, which powers the engine.
- Automatic Systems: Many advanced generators use electronic fuel injection (EFI) systems. These systems optimize fuel delivery, improving startup efficiency and reducing emissions.
- Manual Override: Some older models may require manual adjustments to ensure proper fuel flow.
The transition from cranking to full engine operation happens swiftly, but it’s a critical moment that determines whether the generator starts successfully.
Step 4: Stabilization and Power Generation
After ignition, the engine transitions into a steady operational state. During this phase:
- RPM Stabilization: The engine’s revolutions per minute (RPM) stabilize to the desired level. This ensures consistent power output.
- Load Application: If the generator is connected to a load, the operator must gradually apply the load to avoid sudden stress on the system.
- Monitoring: It is essential to monitor key parameters, such as oil pressure, coolant temperature, and generator output voltage, during the first few minutes of operation.
Proper stabilization ensures the generator runs efficiently and avoids unnecessary wear and tear.
Challenges During Startup and Their Solutions
Starting a diesel generator isn’t always seamless. However, most issues can be addressed with routine maintenance and prompt troubleshooting. Here are some common challenges and their solutions:
- Weak Battery: A weak or discharged battery is one of the most frequent causes of startup failure. Regularly inspect and charge the battery to avoid this issue.
- Air in the Fuel Line: Air pockets can disrupt fuel flow. Bleeding the fuel system ensures smooth startup.
- Cold Weather: Low temperatures can make it harder for diesel fuel to ignite. Using winter-grade diesel and pre-heating systems can mitigate this problem.
Addressing these challenges proactively ensures reliable generator performance even under demanding conditions.
Tips for Efficient Generator Starting
To optimize the starting process, consider the following tips:
- Routine Maintenance: Regularly servicing your generator ensures all components are in good working condition. This includes replacing worn parts, changing oil, and cleaning filters.
- Use High-Quality Diesel: Low-quality fuel can lead to deposits and clogging in the injection system. Always opt for clean, high-grade diesel.
- Test Run Periodically: Running the generator at least once a month keeps the engine lubricated and identifies potential issues early.
By implementing these practices, users can minimize downtime and maximize the reliability of their diesel generator.
Conclusion
Understanding how a diesel generator starts is essential for operators and maintenance teams. From pre-start checks to the stabilization phase, each step plays a crucial role in ensuring seamless operation. Regular maintenance, combined with attention to detail during the startup process, can significantly enhance the longevity and efficiency of the generator.
By following the steps and tips outlined above, you can ensure your diesel generator remains a dependable power source for years to come.